
Agregue un acceso directo a Club de Expertos 

Agregue un acceso directo a Club de Expertos 

Agrega un acceso directo a Club de Expertos: presiona  y luego agrégalo a tu pantalla de inicio.
y luego agrégalo a tu pantalla de inicio.
Al continuar, usted acepta los Términos del servicio y la Política de privacidad de Club de Expertos.

Conozca los artículos desarrollados por nuestros expertos en dermatología pediátrica
Escrito por: Clarence de Belilovsky
Especialidad: Dermatóloga. Responsable de comunicación científica en Laboratorios Expanscience.
Fecha de publicación: 26-11-2021

Escrito por: Clarence de Belilovsky
Especialidad: Dermatóloga. Responsable de comunicación científica en Laboratorios Expanscience.
Fecha de publicación: 26-11-2021

Influence of age on neurotrophic activity of juvenile and adult keratinocytes
While the development of barrier function is well documented, little is known about the interactions between nervous system and skin cells during skin maturation. In particular, the development and the maintenance of nervous fibers during skin maturation in the first age is not known.
The Epidermal nerve endings density in 20 healthy children (7-17 years old), as determined by punch biopsy and suction blister, is more than 3 times higher than that found in similar studies of normal adults. This density is lower in young children than in older children (P < 0.01), with no difference between boys and girls (P = 0.92)

The objectives of our studies were
Mechanoreceptors and nervous fibers are colocalized
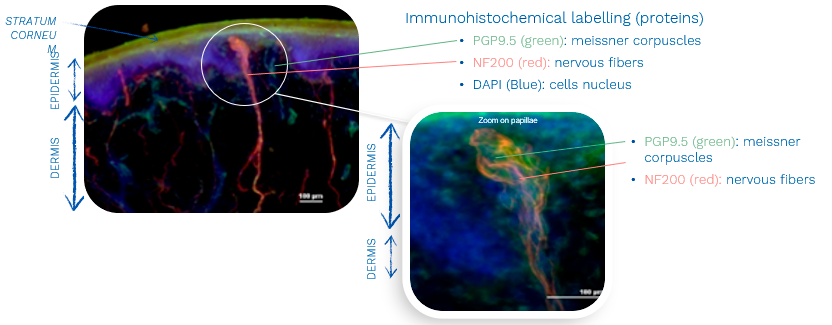
*Obtained from plastic surgery
Construction of cutaneous innervation during infancy: organization
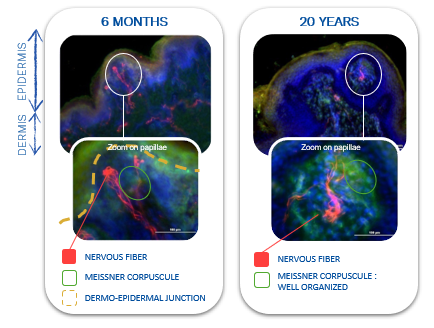
*Obtained from plastic surgery
Meissner corpuscule is less organized in infant than in adult. Maturation of sensorial system in children.
*Obtained from plastic surgery
**Panoutsopoulou IG et al. Muscle Nerve. 2015 ; 51 378-384.
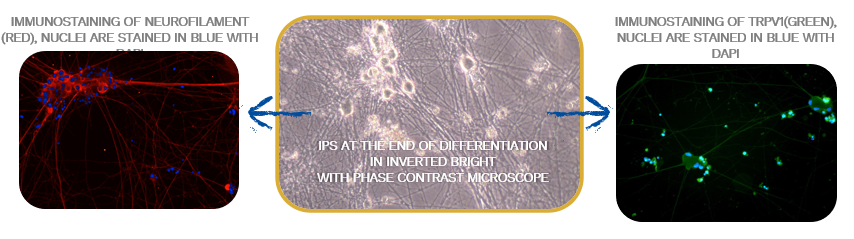
role of keratinocytes -> comparison to adults
Methods: Transcriptomic analysis of skin barrier genes in re-innervated juvenile epidermis vs adults.
Juvenile keratinocytes produce more neuronal trophic factors than adult
Objectives: new model
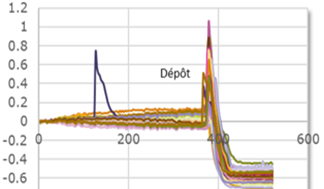
VERIFICATION OF ELECTRIC ACTIVITY AFTER STIMULATION WITH LACTIC ACID
2nd STEP: Innervation of adult epidermis(2)
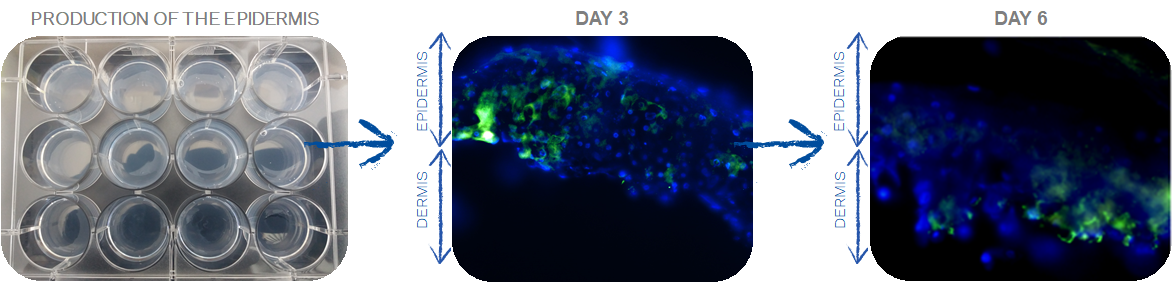
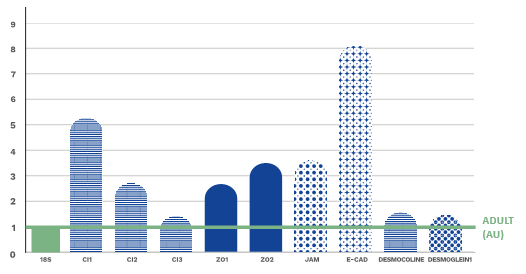
COMPARISON TO ADULTS
Gene expression of claudin (cl) 1-2-3, zonula occludens (zo) 1-2, junctional adhesion
molecule (jam) 1, e-cadherin (e-cad), desmocoline, desmoglein
1 Panoutsopoulou IG, et al. Epidermal innervation in healthy children and adolescents. Muscle Nerve. 2015 ; 51: 378–384.
2 Pr L.Misery Coordinateur et clinicien de centre expert de Dermatologie et Vénérologie CHRU de Brest – Hôpital Morvan, France
No hay comentarios aún.
Comentarios
No hay comentarios aún.